Investigating Haiti and The Dominican Republic
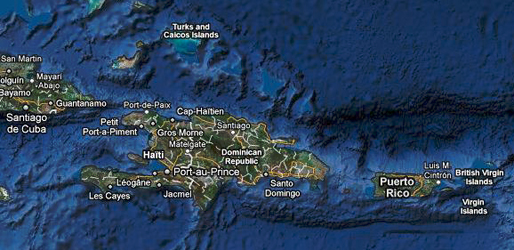
Haiti and Dominican Republic are the two neighboring Caribbean countries which share the border on the island of Hispaniola. The beginning and ending points of the border was established after the 1777 Treaty of Aranjuez, signed by French and Spanish. Both of the countries locate between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean.The Dominican Republic has five mountain ranges run throughout the country includes Cordillera Central, which includes Pico Duarte, the highest mountain in the Caribbean. About 80% of the country is mountainous that has forest cover and fertile soils. The North side of the country has the Cordillera Septentrional range. This range of mountain runs parallel to the Atlantic coast starting from the town of Monte Cristi near the border to the Samara Peninsular in the East.
The Codillera Cenral is the highest range in the Dominican Republic as well as the West Indies. In addition, there are the Sierra de Neiba and the Cordillera Oriental, two dry and rocky ranges. These two mountain ranges run along the Atlantic coast and end in the foothill s of the Cordillera Central.
Dominican Republic has the second largest economy in the Caribbean and Central American region. Most of its income comes from nickel, sugar, coffee, cacao, and industrial raw material.
Haiti is about 2800 square kilometers. It has the size of a third of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola. The eastern edge of the country borders the Dominican Republic. Haiti's mainland has three main regions: the northern region, the central region, and the southern region. Several nearby islands are also parts of Haiti.
The country natural resources include copper, bauxite, calcium carbonate, marble, gold and hydropower. It lies in the middle if the hurricane belt and subject to severe storms, occasional flooding, earthquakes, and periodic droughts.
Haiti is the poorest countries in the Western hemisphere with 80 percent of the population living under the poverty line and 54 percent living in abject poverty.
The difference in the economics of Haiti and Dominican Republic is rooted in a few reasons. One of the reasons is the geography difference of the two countries. The ranges of mountains in the Dominican Republic play a main role in the agriculture of both of the country.
Haiti has drier land due to the lack of rain. Thus, It has less land that is can be used for agriculture. Haiti also has high percentage of the area is mountainous and limestone terrain. Hence, soils are thinner and less fertile and have a lower capacity for recovery.
Dominican Republic receives a higher amount of rain leads to higher rates of plan growth. Thus, the agriculture in Dominican side is more develop compare to Haiti. The high mountain concentration on the Dominican side gives a higher supply of water (eastward). This country also has broad valley, plains, highlands, and thicker soils.
Even though these two neighboring countries have many differences, but they share many similarities in culture. Their cultures are diverse but similar to some extends. Music for instance, Compass and Merengue are really similar. Platanos is the favorite food for both of the countries. They use Platano for most of their dishes from fried, blended, and baked to dried snack. Both Haiti and Dominican Republic are popular tourist destination and the residents are really warm and welcoming toward foreigners.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |








